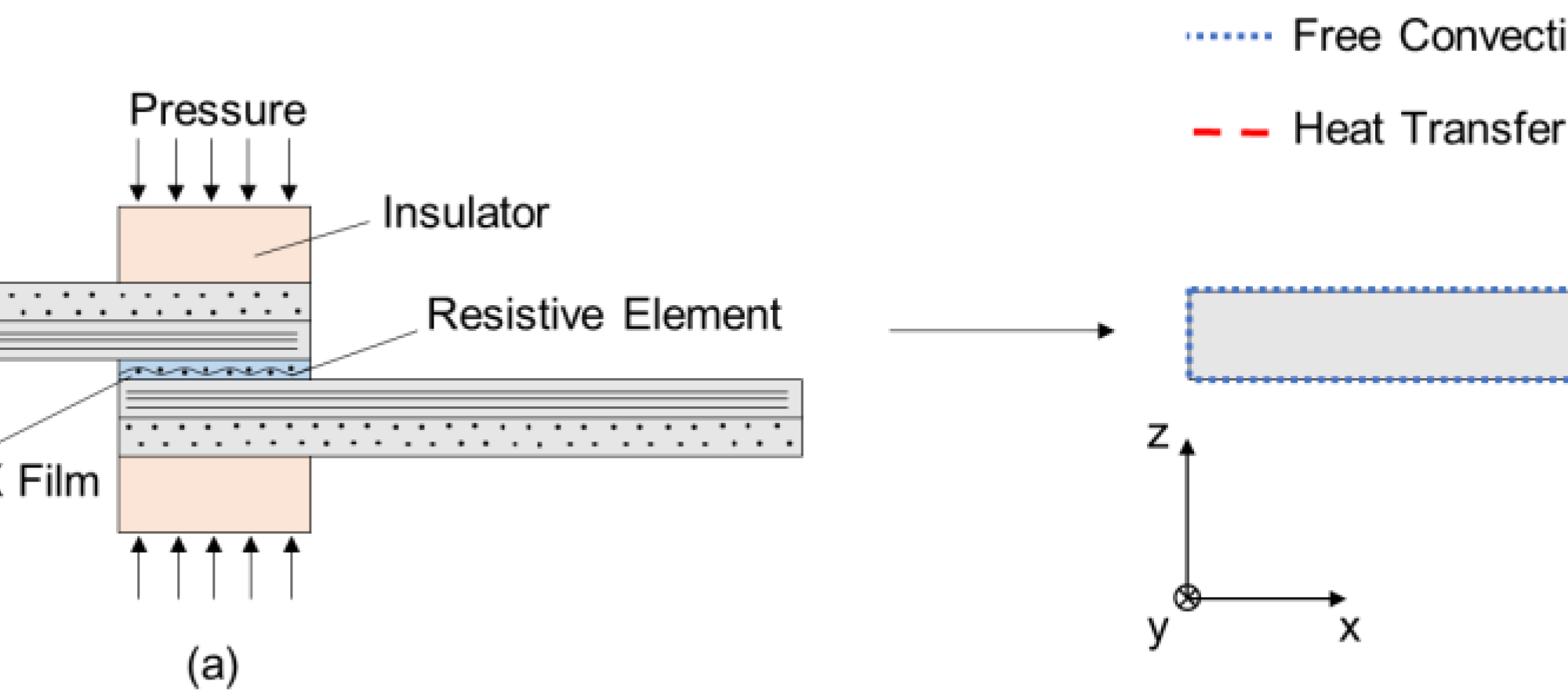
Using thermoplastics as the matrix in carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) offers the possibility to make use of welded joints, which results in weight savings compared to conventional joining methods using mechanical fasteners. In this paper, the resulting temperature distribution in the material due to resistance welding is investigated by transient finite element (FE) simulations. To examine the effects on the component structure, a numerical modeling approach is created, which allows determining the residual stresses caused by the welding process. It is shown that the area of the structure, especially near the joining zone, is highly affected by the process, especially in terms of residual stresses. In particular, the stresses perpendicular to the fiber direction show failure relevant values, which might lead to the formation of microcracks in the matrix. In turn, that is assumed to be critical in terms of the fatigue of welded composite structures. Thus, the suggested modeling approach provides residual stresses that can be used to determine their effects on the strength, structural stability, and fatigue of such composite structures.
Follow the link to the entire article.
- Neuer AFP-Legekopf – Leichtbauproduktion im SCALE: IFW testet erfolgreich neues AFP-System - 5. Juni 2024
- Es ist geschafft! - 19. April 2024
- Besuch der AKAFLIEG Hannover - 11. April 2024